Image by congerdesign from Pixabay
|| Banana Peppers – What is a Banana Pepper? || Top 20 Most Common Types of Edible Peppers || How To Prune Pepper Plants ||
Table of Contents
How To Save Pepper Seeds
Is your pepper plant producing more peppers than you can use? Don’t let those delicious fruits go to waste! Here’s how to harvest pepper seeds from your homegrown plants. Plus, learn about seed viability and storage so you can save those seeds for next year.
One way to save money when gardening is to keep the seeds from your peppers. This can be tricky, as not all pepper seeds are viable, but it is possible with care.
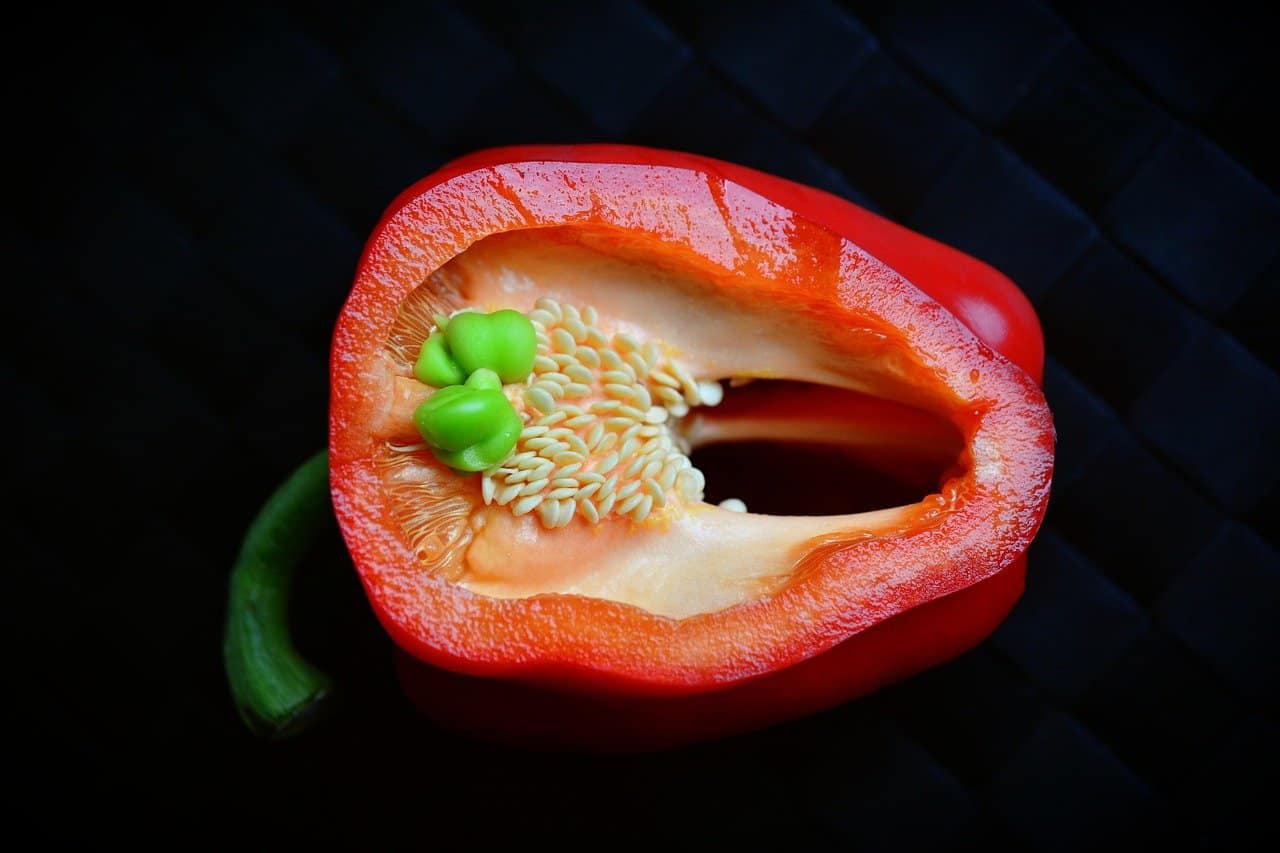
The first step is to choose peppers that are healthy and ripe. Next, cut the pepper open and remove the seeds, careful not to damage them. Next, spread the roots out on a paper towel and let them dry for a few days.
Once they’ve been cooked, store them in an airtight container. Dried. Envelope or container and keep them in a cool, dark place. Then, when it comes time to plant next year, you can simply plant the saved seeds and enjoy fresh peppers without buying new ones!
Pepper Seed Viability
When it comes to growing pepper plants, one of the essential considerations is seed viability. For pepper seeds to germinate and produce healthy plants, they must be viable, which means they must be alive and able to sprout.
Pepper seeds can lose their viability for several reasons, including exposure to extreme temperatures, excessive moisture, or age. If you’re not sure whether your pepper seeds are still viable, there are a few simple tests you can do at home.
One test is to place the seeds on a moist paper towel and see if they sprout within a week or two. Another test is to identify the seeds in a cup of water; if they sink, they’re probably still viable. If you want to be sure, you can also consult a seed testing lab. By making sure your pepper seeds are still feasible before you plant them, you can increase your chances of success.
Pepper seeds can last up to a year if stored properly, although the germination rate will decline. Therefore, it is critical to ensure the best possible probability of success. Therefore, it is recommended that you sow pepper seeds within one year of harvest.
When stored properly, pepper seeds will remain relatively dry and protected from temperature extremes. The ideal storage conditions for pepper seeds are an excellent, dark location with low humidity.
If you cannot store your pepper seeds in these conditions, you can still sow them, but you may have a lower germination rate. When sowing pepper seeds, starting them off in warm soil is essential.
You can sow them straight on the ground or in a container in late spring/early summer or start them Around eight weeks before the newest frost date; bring the plants indoors. After the seedlings have sprouted, thin them out so that only the most vigorous plants remain.
Pepper plants require full sun and well-drained soil to thrive, so choose a planting site that meets these criteria. With care and attention, your pepper plants will produce a bountiful crop of peppers that can be enjoyed for years to come.
How to Harvest Pepper Seeds
Peppers are a warm-weather crop that can be tricky to start from seed. One way to ensure a successful crop is to harvest the seeds from your best peppers and plant them the following year. Here’s how to do it:
Peppers are a tasty and nutritious complement to any meal, but they’re outstanding in chili. Did you know that it’s easy to harvest pepper seeds so you can grow your plants?
First, choose ripe peppers that are free of blemishes or disease. After that, cut the peppers in half lengthwise and remove the seeds. Remove the seeds. Wash the seeds gently in warm water to remove any clinging pulp. To dry the origins, spread them out on a paper towel to absorb the moisture, spread them out. Once they’re dry, store the seeds in a cool, dark place until you’re ready to plant them.
With patience and care, you can quickly harvest pepper seeds to produce a bountiful crop of delicious peppers.
The best time to harvest pepper seeds is after the peppers have ripened and begun to turn red or yellow. After that, open the peppers and remove the seeds. Careful not to damage them.
Rinse the seeds in cool water, and then spread them out on a paper towel to dry. Once they’re completely dry, store the seeds in a cool, dark place until you’re ready to plant them. You can have fun with just a little effort. Fresh peppers all year round!
Proper Pepper Seed Saving
Many gardeners enjoy growing peppers, but did you know that you can save the seeds from your pepper plants to grow next year? Peppers are self-pollinating, which means that the seeds will be faithful to the parent plant.
To save seeds, wait until the peppers are fully ripe. Next, cut the pepper open, remove the seeds, and place them on a paper plate or towel to dry. Once the seeds are dehydrated, store them in a cool, dark place until planting season.
When it comes time to plant, start the seeds indoors about eight weeks before the last frost date; pepper seedlings need warm temperatures to thrive, so keep them in a warm spot and water them regularly. Then, with a bit of care and attention, you can enjoy fresh peppers from your plants for years to come.
Time to Germination
The time it takes for pepper seed to germinate can vary depending on the type of pepper and growing conditions. However, most pepper seeds will germinate within 7-14 days. Peppers need warm temperatures and consistent moisture to germinate.
If the soil is too cold or too dry, it can inhibit or prevent germination altogether. The seedlings must be nurtured after the seeds have germinated. Transplanted into individual pots or raised beds. Pepper seedlings require full sun and should be kept moist but not wet until they are ready to be transplanted into the garden. With proper care and attention, peppers can be a delicious and rewarding addition to any garden.
The temperature and moisture levels also affect the time it takes for a seed to germinate. Seeds will usually germinate more quickly in warm, moist conditions. However, too much heat or moisture can also be harmful to seeds. In general, most seeds will germinate within a few weeks if kept at a temperature of around 20 degrees Celsius and given enough moisture.
Choose Ripe Peppers To Save The Seeds
Peppers come in all shapes, sizes, and colors. Some are sour, some are sweet, while others are salty—plain mild. No matter your preference, there is a pepper out there for you. And, if you want to save the seeds from your favorite pepper to grow next season, it is important to choose a ripe pepper.
Ripe peppers will have soft skin that is easy to pierce. In addition, the stem should be green and fresh-looking, and the pepper should feel heavy for its size. If you can find a pepper that meets all of these criteria, the chances are that the seeds inside will be viable and ready to plant. So, next time you’re at the market, choose a ripe pepper if you want to save the seeds.